Comparative Analysis of Ethereum Layer-2 Solutions: Arbitrum & Polygon
Ethereum’s network, at times, can feel like a congested highway. Layer-2 solutions, in this analogy, act as express lanes, alleviating this congestion and allowing for a smoother flow of transactions. This means more than just speed; businesses benefit from reduced costs, and users enjoy a streamlined experience. Additionally, these solutions are environmentally conscious and uphold the network’s security.
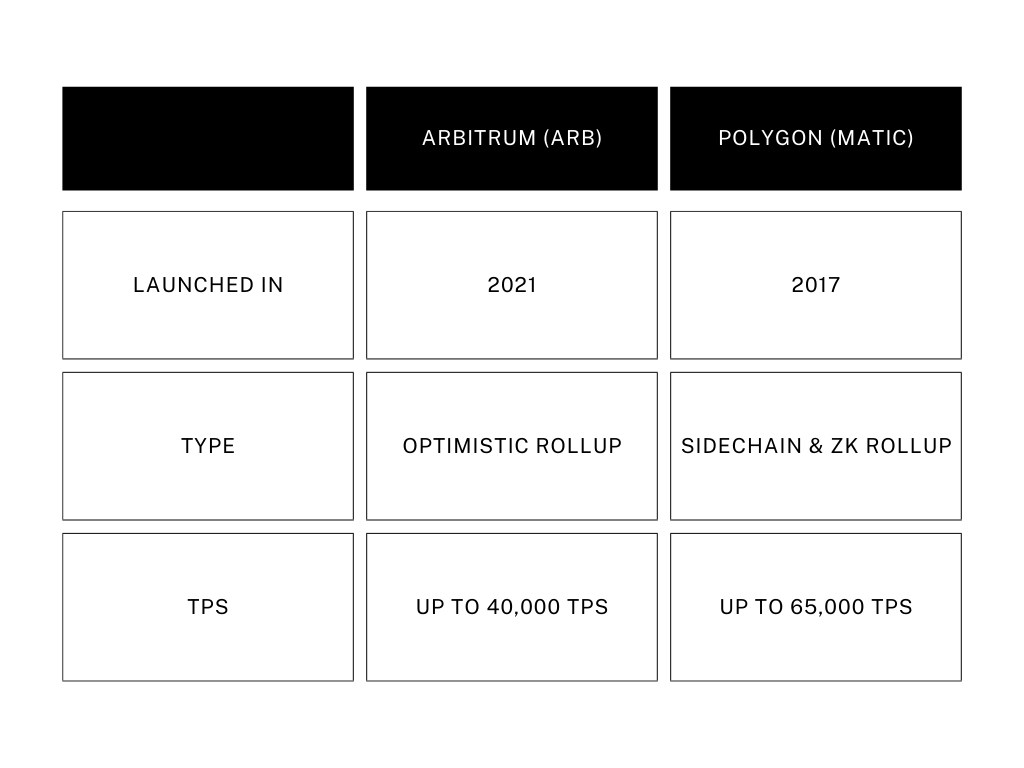
Among the notable contributors to Layer-2 are Arbitrum and Polygon. They effectively address Ethereum’s challenges by enhancing its capacity and trimming fees. For developers, these platforms are robust, providing tools and resources for innovation.
In this blog, we’ll explore the nuances of Arbitrum and Polygon. Alongside this, we’ll discuss how Bitquery delivers insights that are of value to both regular users and developers.
Understanding Arbitrum
Arbitrum, developed by Offchain Labs, serves as a crucial improvement for the Ethereum blockchain, addressing its scalability challenges. By acting as a Layer-2 solution, Arbitrum alleviates congestion on the Ethereum network, akin to adding auxiliary lanes to a busy highway. Furthermore, by reducing computational burdens and bundling multiple transactions, Arbitrum offers an ecosystem where businesses can operate with diminished costs and users can experience expedited transactions.
Now, let’s explore the workings, features, and advantages of Arbitrum in greater detail.
How does Arbitrum work as a Layer-2 solution?
Arbitrum improves Ethereum’s capabilities as a Layer 2 scaling solution by optimizing transactions and computation processes. At its core, Arbitrum uses optimistic rollups to group multiple transactions together off-chain, ensuring that the main Ethereum blockchain remains uncluttered and runs efficiently. This allows for complex computations to be conducted off-chain before they are verified and finalized on the main Ethereum blockchain.
Furthermore, Arbitrum facilitates seamless asset transfers between its Layer 2 and Ethereum mainnet, ensuring interoperability and flexibility in transactions. It also greatly improves the performance of Ethereum smart contracts by undertaking computation and processing tasks off the mainnet, thus speeding up transaction processing times.
Moreover, Arbitrum’s infrastructure allows for the selection of specific validators in the consensus process of Decentralized Applications (DApps), providing a more refined and efficient approach to validation processes. It employs a batching technique where multiple transactions are grouped together before being published to the main blockchain, a strategy that is instrumental in enhancing scalability and reducing transaction costs.
Through these mechanisms, Arbitrum significantly boosts the scalability, efficiency, and functionality of the Ethereum blockchain, acting as a powerful and essential Layer 2 scaling solution.
Key Features
Now, let’s dive deeper into the prominent features of Arbitrum:
-
EVM Compatibility: Arbitrum boasts high compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing for seamless integration and operation with Ethereum-based applications.
-
Scalability: Arbitrum is designed to handle a high volume of transactions, thereby addressing one of the major challenges faced by many blockchains today.
-
Security Council Voting by ARB Token Holders: Those holding the ARB token have a say in the network’s governance by being able to vote on electing members to the Security Council, ensuring a decentralized decision-making process.
Advantages
Let’s move on to the notable benefits of Arbitrum:
-
High Throughput for DApps: Developers can run Ethereum decentralized applications (DApps) on Arbitrum with significantly lower transfer fees and higher transaction speeds, without the need for modifications.
-
Cost-Effective & Fast: Compared to Ethereum’s 14 transactions per second, Arbitrum can process up to 40,000 transactions per second. Moreover, while Ethereum transactions can be expensive, Arbitrum’s transactions can be executed for just a fraction of the cost—sometimes only a few cents.
-
Robust Developer Tooling: Developers are provided with a set of tools that facilitate the creation, testing, and deployment of applications on Arbitrum.
Also Read: Arbitrum API - Tokens, NFTs, DEX, Balances & More
Understanding Polygon
Polygon, formerly known as MATIC network, is a versatile blockchain platform founded by Sandeep Nailwal, Jaynti Kanani, and Anurag Arjun in 2017. It’s like a one-stop-shop for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchains, making transactions faster and cheaper, and enhancing the overall flexibility and scalability of blockchain projects. Despite its evolution, Polygon’s cryptocurrency continues to be called the MATIC coin. Its design ensures that users can interact with decentralized applications (DApps) smoothly, without getting bogged down by network congestion.
Now, let’s explore the workings, features, and advantages of Polygon in greater detail.
How does Polygon work as a Layer-2 solution?
Polygon operates as a Layer-2 (L2) solution to enhance and scale the Ethereum network. Its multifaceted approach revolves around sidechains, interoperability, enhanced chain performance, and a robust validator network.
Firstly, Polygon leverages sidechains that seamlessly interact with Ethereum, creating an auxiliary network that is both compatible and independent. These sidechains introduce significant improvements in transaction speed and cost-effectiveness.
One of Polygon’s key features is its use of a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which enhances the scalability of the network. This PoS approach allows transactions to be validated by a network of validators off-chain before finalizing them on Ethereum’s primary chain. This reduces the strain on the Ethereum network, resulting in faster transactions and reduced gas fees.
The long-term vision of Polygon, known as Polygon 2.0, aims to provide tailored scaling solutions for various use cases. These chains will be interoperable, enabling near-instant cross-chain transactions without requiring a bridge to Ethereum, thanks to the utilization of ZK proofs.
Additionally, Polygon CDK (Chain Development Kit) empowers developers to deploy their own ZK-powered L2 solutions, tailored to specific use cases. These appchains are modular and configurable for performance and cost, ensuring interoperability with other Polygon CDK chains.
Key features
Polygon stands out as a scaling solution with a wide array of key features:
-
Scalability: Polygon excels in scalability, capable of supporting millions of users and transactions at a minimal cost. This scalability is crucial for accommodating the growing demand for blockchain applications.
-
Sidechains: Polygon’s innovative use of sidechains, which are parallel blockchains, enables faster and more cost-effective transactions. These sidechains operate alongside the Ethereum mainnet, alleviating congestion and reducing fees.
-
Interoperability & Cross-Chain Compatibility: Polygon fosters interoperability and cross-chain compatibility, allowing seamless interaction with other blockchain networks and assets.
Advantages
Let’s move on to the notable benefits of Polygon:
-
Improved User Experience: Polygon is designed to offer an improved user experience, making it more accessible and user-friendly for both developers and end-users.
-
Carbon Neutrality: Polygon is committed to environmental sustainability and aims to achieve carbon neutrality. Moreover, it has plans to go beyond neutrality and become climate positive, contributing positively to the environment.
-
Lower Transaction Costs: Transactions on Polygon are cost-efficient, addressing one of the significant challenges faced by many blockchain users.
-
Play-to-Earn Gaming: Polygon’s fast transaction processing speeds, make it an ideal platform for play-to-earn gaming, enhancing the gaming experience.
Comparative Analysis using Bitquery APIs
Now, let’s dive deeper into Polygon and Arbitrum, exploring some more technical insights using Bitquery.
How to Get Started with Bitquery?
To get started for free, please create an account here with your email: GraphQL IDE
Once created, create your first query. Join the telegram group for any doubts and support. To learn more about how to use the Bitquery API, please see the following resources:
Historical / Near-Realtime Chain Data: Blockchain API Documentation (V1 Graphql Docs) | Blockchain Graphql API (V1 API Docs)
Realtime Data , Websocket and Cloud Product: Blockchain Streaming API (V2 Graphql Docs) | Streaming API (V2 API Docs)
Let’s dive into on-chain insights with Bitquery APIs.
Top Traded Tokens
We can also utilize the Bitquery API to view the most traded tokens on a specific blockchain network.
Below is the query to display the top 2 traded tokens on Arbitrum from October 10, 2023, onwards.
{
EVM(dataset: combined, network: arbitrum) {
DEXTrades(
limit: {count: 10}
orderBy: {descendingByField: "count"}
where: {Block: {Date: {since: "2023-08-01"}}}
) {
count
Trade {
Buy {
Currency {
Name
Symbol
SmartContract
}
}
}
}
}
}
Output:

Latest Uniswap Trades
We can also utilize the Bitquery API to view the latest Uniswap trades on a blockchain network. In the code below, we showcase the most recent Uniswap trades from the past week on the Polygon Network.
query ($network: EthereumNetwork!, $limit: Int!, $offset: Int!, $exchange: String!, $from: ISO8601DateTime, $till: ISO8601DateTime) {
ethereum(network: $network) {
dexTrades(
options: {desc: ["block.height", "tradeIndex"], limit: $limit, offset: $offset}
date: {since: $from, till: $till}
exchangeName: {is: $exchange}
) {
block {
timestamp {
time(format: "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
}
height
}
tradeIndex
protocol
exchange {
fullName
}
smartContract {
address {
address
annotation
}
}
buyAmount
buy_amount_usd: buyAmount(in: USD)
buyCurrency {
address
symbol
}
sellAmount
sell_amount_usd: sellAmount(in: USD)
sellCurrency {
address
symbol
}
transaction {
hash
}
}
}
}
# parameters
{
"limit": 10,
"offset": 0,
"network": "matic",
"exchange": "Uniswap v3",
"from": "2023-05-19",
"till": "2023-05-26T23:59:59",
"dateFormat": "%Y-%m-%d"
}
Output:

Also Read: Uniswap API: Get Pools Data, Tokens and Create Charts
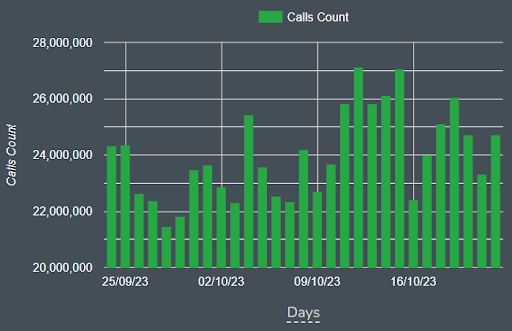
Number of Smart Contract Calls
We can also utilize the Bitquery explorer to view the total number of smart contract calls on a blockchain network. In the screenshot below, we see the number of smart contract calls on Polygon Network over the past month.
Monthly Transaction Volume
We can also view the monthly transaction volume using Bitquery APIs. In the code below, users can see the monthly transaction volumes for the Polygon network.
{
ethereum(network: matic) {
transactions(
options: {asc: "date.month"}
date: {since: "2023-01-01"}
) {
date {
month
year
}
count: count
gasValue
}
}
}
Output:

Latest Trades for a Specific token
We can also view the latest trades of a specific token on a particular blockchain network. In the query below, we see the recent trades of the Dino token on the Polygon network.
{
ethereum(network: matic) {
dexTrades(
options: {desc: ["block.height", "tradeIndex"], limit: 10}
baseCurrency: {is: "0xaa9654becca45b5bdfa5ac646c939c62b527d394"}
date: {after: "2023-03-28"}
) {
transaction {
hash
}
exchange {
name
}
tradeIndex
date {
date
}
block {
height
}
buyAmount
buyAmountInUsd: buyAmount(in: USD)
buyCurrency {
symbol
address
}
sellAmount
sellAmountInUsd: sellAmount(in: USD)
sellCurrency {
symbol
address
}
sellAmountInUsd: sellAmount(in: USD)
tradeAmount(in: USD)
transaction {
gasValue
gasPrice
gas
}
}
}
}
Output:

Number of Active Users
We can also view the number of active users on a specific blockchain network. This information is crucial for developers looking to deploy their dapps on active chains. In the query below, we can see the number of active users on Arbitrum.
{
EVM(network: arbitrum, dataset: combined) {
Transactions(where: {Block: {Date: {till: "2023-10-18", since: "2023-10-11"}}}) {
ChainId
Block {
Date
}
senders: uniq(of: Transaction_From)
}
}
}
Output:

Number of Contracts Deployed Daily
With Bitquery, we can also monitor the number of contracts deployed daily. The query below displays the daily count of contracts deployed on Arbitrum.
{
EVM(network: arbitrum, dataset: combined) {
Calls(where: {Call: {Create: true}}, orderBy: {descendingByField: "Block_Date"}) {
Block {
Date
}
count
}
}
}

Top NFT Marketplaces
We can view the top NFT marketplaces on specific blockchain networks. Below is the query to identify the leading NFT marketplaces on Arbitrum.
{
EVM(dataset: combined, network: arbitrum) {
DEXTrades(
orderBy: {descendingByField: "count"}
limit: {count: 10}
where: {Block: {Date: {since: "2023-08-01", till: "2023-08-10"}}, Trade: {Buy: {Currency: {Fungible: false}}, Sell: {Currency: {Fungible: true}}}}
) {
Trade {
Dex {
OwnerAddress
SmartContract
ProtocolName
ProtocolFamily
ProtocolVersion
}
}
nfts: uniq(of: Trade_Buy_Currency_SmartContract, method: approximate)
currencies: uniq(of: Trade_Sell_Currency_SmartContract, method: approximate)
buyers: uniq(of: Trade_Buy_Buyer, method: approximate)
count
ChainId
}
}
}
Output:

Also Read: Top NFT Data Sources
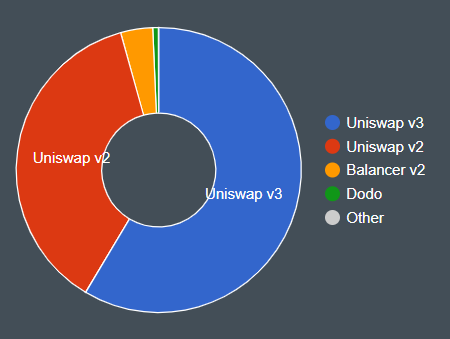
Total DEX Trades By Protocol
Users can also view the total DEX trades by protocol for a blockchain network using the Bitquery Explorer. In the screenshot below, we showcase the total DEX trades by protocol on the Polygon network over the past month.
Number of Transactions
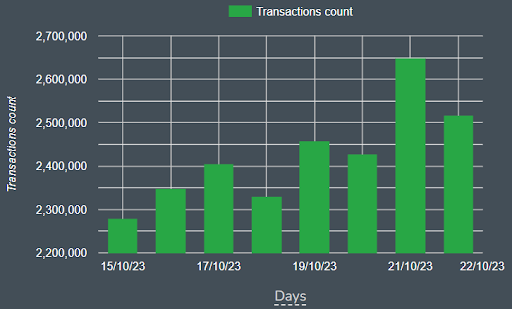
Users can also utilize the Bitquery explorer to view the latest transactions on the blockchain network, assisting them in determining whether the chain is active or a ghost chain.
Below is the data from Bitquery explorer, showcasing the total number of transactions that took place on the Polygon Network from October 15th to 22nd.
Conclusion
In summary, Arbitrum and Polygon, as Layer 2 scaling solutions, enhance Ethereum’s capabilities by processing transactions off-chain, reducing costs, and improving speed. Arbitrum excels in offering lower fees and EVM compatibility, while Polygon stands out with its impressive speed and versatility across various applications. Both solutions leverage Ethereum’s security features, further contributing to the Ethereum ecosystem’s evolution. If you are a developer, trader, or user, you can utilize Bitquery APIs to dive deeper into these Layer 2 solutions and determine which one is best suited for you or your application.
About Bitquery
Bitquery is your comprehensive toolkit designed with developers in mind, simplifying blockchain data access. Our products offer practical advantages and flexibility.
-
APIs - Explore API: Easily retrieve precise real-time and historical data for over 40 blockchains using GraphQL. Seamlessly integrate blockchain data into your applications, making data-driven decisions effortless.
-
Coinpath® - Try Coinpath: Streamline compliance and crypto investigations by tracing money movements across 40+ blockchains. Gain insights for efficient decision-making.
-
Data in Cloud - Try Demo Bucket: Access indexed blockchain data cost-effectively and at scale for your data pipeline. We currently support Ethereum, BSC, Solana, with more blockchains on the horizon, simplifying your data access.
-
Explorer - Try Explorer: Discover an intuitive platform for exploring data from 40+ blockchains. Visualize data, generate queries, and integrate effortlessly into your applications.
Bitquery empowers developers with straightforward blockchain data tools. If you have questions or need assistance, connect with us on our Telegram channel. Stay updated on the latest in cryptocurrency by subscribing to our newsletter below.
If you enjoyed this blog post, you might also find our article on Arbitrum Ecosystem interesting.
Post written by guest author Yash
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe and never miss any updates related to our APIs, new developments & latest news etc. Our newsletter is sent once a week on Monday.


